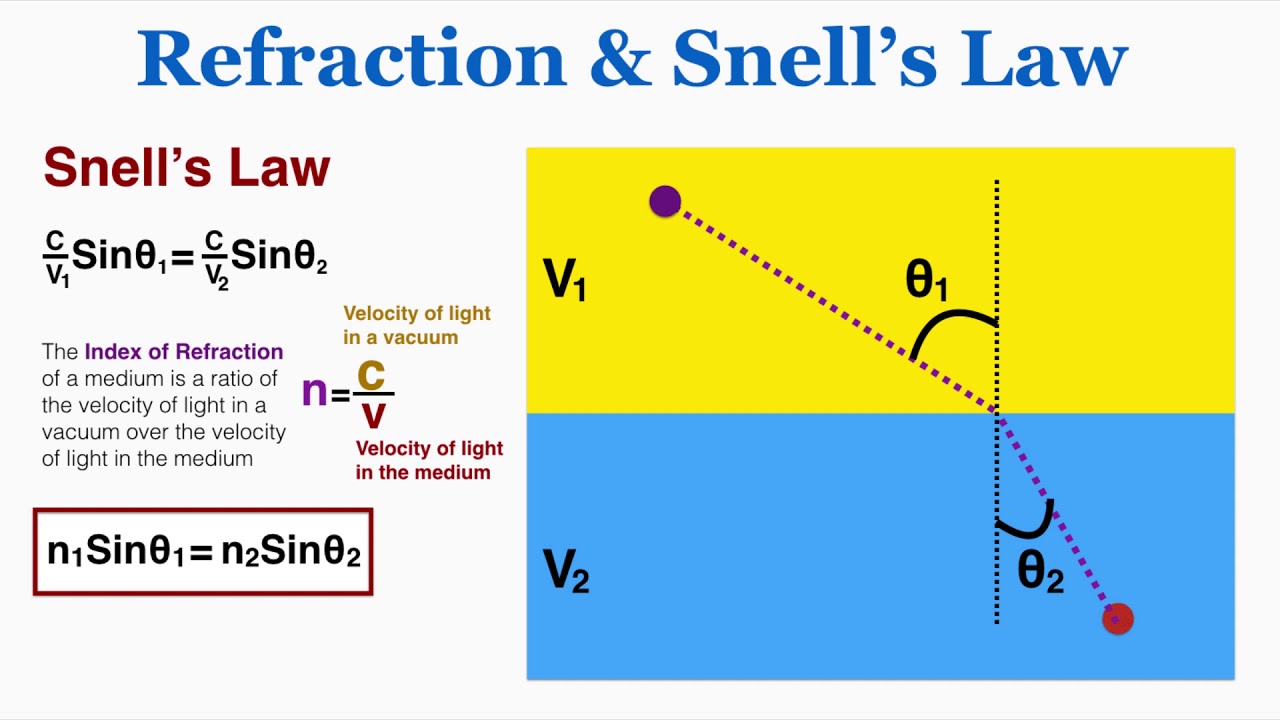
Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves . The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2d and 3d. Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums according to a relationship called. R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. The same logic holds for reflected waves: Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one medium to another. Web this is known as snell’s law. Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves?
from www.youtube.com
The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2d and 3d. 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. The same logic holds for reflected waves: Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one medium to another. Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums according to a relationship called. Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. Web this is known as snell’s law.
Refraction and Snell's Law IB Physics YouTube
Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves The same logic holds for reflected waves: 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2d and 3d. Web this is known as snell’s law. The same logic holds for reflected waves: Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums according to a relationship called. R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one medium to another.
From arachnoid.com
Snell's Law Calculator Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves The same logic holds for reflected waves: 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one medium to another. Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. Web the. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From exodwppwl.blob.core.windows.net
Optics Ray Explained at Jason Dixon blog Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2d and 3d. Web this is known as snell’s law. 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. The same logic holds for reflected waves: Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web snell's law. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From www.youtube.com
Waves Refraction and Snell's Law YouTube Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2d and 3d. 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? The same logic holds for reflected waves: R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Continuity of what wave parameter is. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From alluxa.com
Angle of Incidence (AOI) and Polarization Alluxa Optical Filters and Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums according to a relationship called. Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one medium to another. Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. The same logic holds for reflected waves:. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From www.youtube.com
Refraction and Snell's Law IB Physics YouTube Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2d and 3d. R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums according to a relationship called. 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. Continuity of what wave. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From www.researchgate.net
5 Snell's law ray transmission and total internal reflection on the Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. The same logic holds for reflected waves: 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one medium to another. Web this is known as snell’s law. The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From sciencenotes.org
Refraction Definition, Refractive Index, Snell's Law Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums according to a relationship called. R is the same and λ is the same (since. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From answercampuschadwick.z21.web.core.windows.net
Give And Explain The Snell's Law Equation Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2d and 3d. R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Oblique Incidence Snell’s Laws PowerPoint Presentation, free Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2d and 3d. 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From galileo-unbound.blog
Snell’s Law The FiveFold Way Galileo Unbound Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one medium to another. Web this is known as. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From byjus.com
What is Snell's law for reflection and refraction? Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one medium to another. Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums according to a relationship called. The same logic holds for reflected waves: The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From discover.hubpages.com
The Basis of Interference (EMI) Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web this is known as snell’s law. 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2d and 3d. Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From www.reddit.com
snell's law example problem no.1 with solution (snell's law, module 33. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves The same logic holds for reflected waves: Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums according to a relationship called. Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From byjus.com
What is snell's law? Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums according to a relationship called. R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web snell's law is a formula used to describe. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web this is known as snell’s law. Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 23 Fresnel equations PowerPoint Presentation, free Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves Continuity of what wave parameter is responsible for reflection. Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? Web the degree of refraction or bending depends on the relative refractive indices of the two mediums according to a relationship called. 2d and 3d waves, snell’s law. Web this is known as snell’s law. The main focus. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From www.youtube.com
Refraction of a Plane Wave by the use of Wave Theory Snell's Law Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves The same logic holds for reflected waves: R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one medium to another. Web the degree of. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.
From answercampuschadwick.z21.web.core.windows.net
Give And Explain The Snell's Law Equation Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves Web what is the basic principle behind the boundary conditions for em waves? The main focus of the lecture is the mathematical description of 2d and 3d. R is the same and λ is the same (since n1=n2 for a reflection). Web snell's law is a formula used to describe how light refracts, or bends, when it passes from one. Snell's Law Electromagnetic Waves.